13
Generators vs Extractors: Uses and Benefits
Learn the difference between generators and extractors, their practical uses, and when each tool is most useful for data, code, and SEO tasks.
Generators vs. Extractors: What They’re Used For and When They’re Useful
Introduction: The Tools Behind Digital Efficiency
In the digital world, productivity often depends on having the right tools at your disposal. Two categories that frequently come up are generators and extractors. At first glance, they might seem similar—both automate tasks and save time. But in reality, they serve very different purposes.
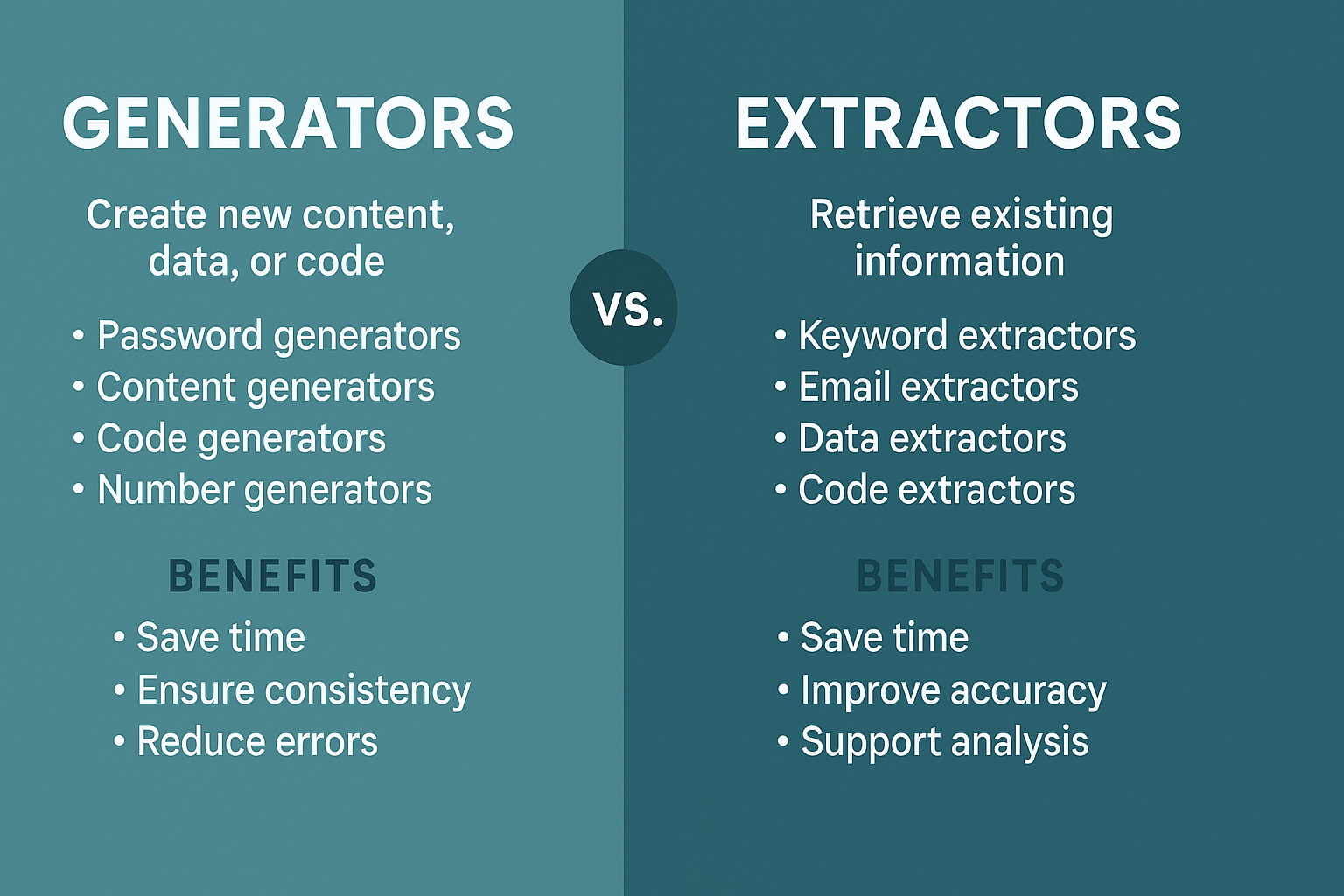
- Generators create new content, data, or code.
- Extractors pull out existing information from sources.
Understanding when to use generators vs extractors can make a huge difference in efficiency, accuracy, and even SEO results. This article will break down what each tool does, provide examples, and guide you on when to use them effectively.
What Are Generators?
Definition
A generator is a tool that produces or creates something new automatically, based on rules, templates, or algorithms.
Examples of Generators
- Password Generators: Create strong, random passwords.
- Content Generators: Produce blog outlines, product descriptions, or meta tags.
- Code Generators: Write boilerplate code in frameworks.
- Number Generators: Generate random values for testing or gaming.
Benefits of Generators
- Save time by automating repetitive tasks.
- Ensure consistency (e.g., generating IDs or tokens).
- Reduce human error.
What Are Extractors?
Definition
An extractor is a tool that retrieves existing information from structured or unstructured data.
Examples of Extractors
- Keyword Extractors: Identify relevant keywords from text.
- Email Extractors: Collect email addresses from websites.
- Data Extractors: Pull information from PDFs, spreadsheets, or APIs.
- Code Extractors: Isolate functions, classes, or dependencies.
Benefits of Extractors
- Save time when gathering large volumes of data.
- Improve accuracy by automating information retrieval.
- Support analysis by pulling out patterns or insights.
Generators vs Extractors: Key Differences
FeatureGeneratorsExtractorsPurpose | Create new content or data | Retrieve existing information
Input Needed | Rules, templates, or seed data | Existing content, files, or sources
Examples | Password generator, content generator | Keyword extractor, email extractor
Use Case | Production & automation | Research & analysis
When to Use Generators
1. Creating Strong Passwords
Instead of reusing weak passwords, a generator creates unique, secure credentials.
2. Producing Content at Scale
Marketers use generators to create meta descriptions, titles, or ad copy quickly.
3. Coding Efficiency
Developers rely on code generators to produce boilerplate structures, saving hours of manual setup.
4. Testing Scenarios
QA teams generate random test data (names, numbers, strings) to simulate real-world cases.
When to Use Extractors
1. SEO Keyword Research
A keyword extractor pulls the most relevant terms from competitor content or user queries.
2. Email Prospecting
Sales teams use email extractors to collect leads directly from websites or LinkedIn.
3. Data Mining and Analysis
Researchers extract structured data (like tables) from PDFs or web pages for analysis.
4. Cleaning Content
Extractors remove duplicates, filter important elements, or isolate key insights from large datasets.
Step-by-Step Guide: Choosing Between Generators and Extractors
Step 1: Define Your Goal
- Do you want to create something new? → Use a Generator.
- Do you want to pull information out? → Use an Extractor.
Step 2: Pick the Right Tool
- For content creation → Meta tag generators, blog idea generators.
- For SEO research → Keyword extractors, SERP data extractors.
Step 3: Validate Output
- Generators → Check for relevance and accuracy.
- Extractors → Ensure data is clean and complete.
Step 4: Integrate Into Workflow
Combine generators and extractors where possible. For example:
- Extract keywords from competitors → Use them in a meta description generator.
Real-World Examples
Digital Marketing
- Generator: Create SEO-friendly blog titles.
- Extractor: Pull trending keywords from Google Search Console.
Software Development
- Generator: Auto-generate CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) functions.
- Extractor: Identify dependencies in third-party libraries.
Business Intelligence
- Generator: Create simulation datasets for models.
- Extractor: Pull KPIs from raw database logs.
Tools You Can Use
Popular Generators
- Strong Password Generator – For security.
- Portent’s Idea Generator – For blog titles.
- Yeoman – For scaffolding web apps.
Popular Extractors
- Octoparse – Data extraction from websites.
- SEO Review Tools Keyword Extractor – For SEO research.
- Email Extractor Lite – For lead generation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-Reliance on Generators
Generated content should be edited for tone, accuracy, and uniqueness. - Unethical Data Extraction
Scraping or extracting private data without permission can lead to legal issues. - Ignoring Validation
Always double-check the results of both generators and extractors. - Mixing Up Tool Use Cases
Trying to extract when you should generate—or vice versa—wastes time and leads to poor results.
Advanced SEO Use Case: Combining Both
- Step 1: Use a keyword extractor to pull high-value terms from competitors.
- Step 2: Feed those keywords into a meta description generator.
- Step 3: Optimize generated descriptions manually for maximum impact.
This hybrid approach boosts efficiency while maintaining quality.
Future of Generators and Extractors
With advances in AI and automation, both generators and extractors are becoming more powerful:
- AI Generators: Produce entire blog drafts, code, or visuals.
- AI Extractors: Identify sentiment, extract structured data, and clean datasets automatically.
The future lies in tools that blend generation and extraction seamlessly for end-to-end workflows.
Conclusion: The Right Tool for the Right Job
Generators and extractors both play crucial roles in digital work. The key difference lies in intent:
- Use generators when you need to create new data, content, or code.
- Use extractors when you need to pull out useful information from existing sources.
Call to Action: Evaluate your current workflows. Are you wasting time creating content manually or extracting data by hand? Start using generators and extractors strategically to boost efficiency, accuracy, and SEO performance today.
Contact
Missing something?
Feel free to request missing tools or give some feedback using our contact form.
Contact Us